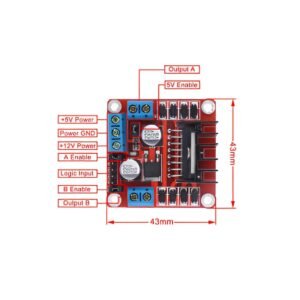
Description
- Motor Specifications:
- Size: Nema 17 (42mm x 42mm)
- Step Angle: Typically 1.8 degrees per step (200 steps per revolution)
- Holding Torque: Varies based on the specific motor model, commonly ranging from 0.4 Nm to 0.6 Nm
- Voltage and Current Rating: Depends on the motor winding and driver configuration, usually between 2V to 4V and 1A to 2A per phase
- Driver Specifications:
- Microstepping Resolution: Adjustable microstepping settings (e.g., full-step, half-step, 1/4-step, 1/8-step, 1/16-step) for smoother motion and improved positional accuracy
- Current Control: Adjustable current limiting to optimize motor performance and prevent overheating
- Step and Direction Control: Compatible with standard step and direction signals from microcontrollers, motion controllers, or CNC controllers
- Protection Features: Overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and reverse polarity protection for safe and reliable operation
- Features and Benefits:
- Precise Motion Control: The Nema 17 stepper motor with driver provides precise control over motion and positioning, enabling accurate and repeatable movement in applications requiring fine-tuned control.
- High Torque: With high holding torque capabilities, this motor and driver combination delivers sufficient force to move loads efficiently, making it suitable for tasks requiring substantial torque.
- Easy Integration: The compact size and standardized mounting features of Nema 17 motors simplify integration into various mechanical systems, while the plug-and-play design of the driver facilitates straightforward installation and setup.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications including 3D printers, CNC machines, robotics, automation equipment, camera sliders, and more, offering versatility and adaptability to different project requirements.
- Applications:
- 3D Printing: Used for precise control of X, Y, and Z-axis movements in 3D printers, ensuring accurate layer deposition and dimensional accuracy in printed parts.
- CNC Machining: Employed in CNC routers, mills, and engravers for controlling tool movement and positioning, enabling accurate machining operations and intricate designs.
- Robotics: Integrated into robotic arms, joints, and actuators for controlling movement and manipulation tasks with precision and reliability.
- Automation Systems: Utilized in various automation systems and machinery for controlling conveyor belts, linear actuators, and other motion components with repeatable accuracy.
- Considerations:
- Voltage and Current Compatibility: Ensure that the motor and driver specifications match the voltage and current requirements of the application to prevent overheating and motor damage.
- Microstepping Settings: Adjust the microstepping settings on the driver to achieve the desired balance between smooth motion and torque output, considering the specific requirements of the application.
- Cooling and Heat Dissipation: Provide adequate cooling measures such as heat sinks or fans to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially in high-current or continuous-duty applications.